What's new in Cubase VST 5.0 ?

![]() All Cubase versions can record audio in 24 bit resolution. Where previously the standard and Score versions were limited to 16 bit recording, all Cbase VST 5.0 versions can record 24 bit audio (provided you have a suitable audio card). See "Selecting Recording Resolution".
All Cubase versions can record audio in 24 bit resolution. Where previously the standard and Score versions were limited to 16 bit recording, all Cbase VST 5.0 versions can record 24 bit audio (provided you have a suitable audio card). See "Selecting Recording Resolution".
![]() Cubase VST/24 replaced by Cubase VST/32. Cubase VST/32 is the new top of the line Cubase VST program. It allows recording and play-back of 32 bit floating point audio files that practically are impossible to overload. This is es-pecially useful for mixdown of audio or virtual synth Tracks, where previously even a simple
clip would ruin the mixdown. Additionally, the 32 bit float file format maintains an incredible
dynamic range that otherwise be lost. See "32 Bit Recording".
Cubase VST/24 replaced by Cubase VST/32. Cubase VST/32 is the new top of the line Cubase VST program. It allows recording and play-back of 32 bit floating point audio files that practically are impossible to overload. This is es-pecially useful for mixdown of audio or virtual synth Tracks, where previously even a simple
clip would ruin the mixdown. Additionally, the 32 bit float file format maintains an incredible
dynamic range that otherwise be lost. See "32 Bit Recording".
![]() Cubase VST now includes dithering. The new dithering options ensure a smooth high quality transition when mixing down to a 16 bit file (for example when preparing to burn a CD). See "Using Dither".
Cubase VST now includes dithering. The new dithering options ensure a smooth high quality transition when mixing down to a 16 bit file (for example when preparing to burn a CD). See "Using Dither".
![]() Cubase VST/32 includes Apogee UV22 Dithering. The Cubase VST/32 goes one step further and includes the industry acclaimed UV22 dithering algorithm from Apogee. See "Using Dither".
Cubase VST/32 includes Apogee UV22 Dithering. The Cubase VST/32 goes one step further and includes the industry acclaimed UV22 dithering algorithm from Apogee. See "Using Dither".
![]() All Cubase VST versions include support for Live Internet Sessions. Cubase VST can now be used live with other Cubase users on the Net with the InWire system supported by the Rocket Network. This is described in the separate document "Using Cubase VST with RocketPower".
All Cubase VST versions include support for Live Internet Sessions. Cubase VST can now be used live with other Cubase users on the Net with the InWire system supported by the Rocket Network. This is described in the separate document "Using Cubase VST with RocketPower".
![]() Cubase VST decodes MP3. Cubase VST will import MP3 files and convert them to Wave files directly on import (see
"Using the Import Audio function"). With the optional MP3 encoder plug component, Cubase VST can also export directly to MP3.
Cubase VST decodes MP3. Cubase VST will import MP3 files and convert them to Wave files directly on import (see
"Using the Import Audio function"). With the optional MP3 encoder plug component, Cubase VST can also export directly to MP3.
![]() Cubase VST/32 sounds uniquely analog. Cubase VST/32 features the TrueTape? recording process, bringing the warm sound of analog tape machines to the cool world of precision digital recording.
See "TrueTape 32 Bit Recording".
Cubase VST/32 sounds uniquely analog. Cubase VST/32 features the TrueTape? recording process, bringing the warm sound of analog tape machines to the cool world of precision digital recording.
See "TrueTape 32 Bit Recording".
![]() Window sets available for all main windows. You can save the positions and settings of the main Cubase windows (Arrange Windows, MIDI and Audio Editors, VST windows, the Transport Bar, etc.) as Window Sets. These Window Sets can be recalled at any time, allowing for quick switching between different "work
layouts". See "About Window Sets".
Window sets available for all main windows. You can save the positions and settings of the main Cubase windows (Arrange Windows, MIDI and Audio Editors, VST windows, the Transport Bar, etc.) as Window Sets. These Window Sets can be recalled at any time, allowing for quick switching between different "work
layouts". See "About Window Sets".
![]() Pistes de Dossiers.
Pistes de Dossiers.  Folder Tracks. A Folder Track is a folder in the Arrange window, in which you can put Tracks or other folders. By moving Tracks into different folders, you can structure and organize your Arrangement,
mute and edit several Tracks at a time, etc. Furthermore, you can gain working space on screen by "closing" Folder Tracks (you will still get a graphical overview of the Parts in the folders). Read more in the chapter "Folder Tracks".
Folder Tracks. A Folder Track is a folder in the Arrange window, in which you can put Tracks or other folders. By moving Tracks into different folders, you can structure and organize your Arrangement,
mute and edit several Tracks at a time, etc. Furthermore, you can gain working space on screen by "closing" Folder Tracks (you will still get a graphical overview of the Parts in the folders). Read more in the chapter "Folder Tracks".
![]() Drag and drop Parts and Events between Cubase VST windows and the desktop. Any number of selected parts can be dragged from the Arrangement to the desktop, thereby creating objects that can be dragged back into any Arrange Window. This way you can build a library of the things you use often. See page 347 in the printed Getting Started book.
Drag and drop Parts and Events between Cubase VST windows and the desktop. Any number of selected parts can be dragged from the Arrangement to the desktop, thereby creating objects that can be dragged back into any Arrange Window. This way you can build a library of the things you use often. See page 347 in the printed Getting Started book.
![]() Drag and drop between Cubase windows. Parts can be dragged directly into open editors where the content of the part is placed at the dropped position. Selected notes from editors can be dragged to the arrange window where a part will be made.
Drag and drop between Cubase windows. Parts can be dragged directly into open editors where the content of the part is placed at the dropped position. Selected notes from editors can be dragged to the arrange window where a part will be made.
![]()
 Selection Range Tool.
This tool allows you to make selections in the Arrangement, regardless of Part boundaries. Selected ranges can be moved, cut, copied etc, or processed with various functions. See page 171 in the Getting Started book.
Selection Range Tool.
This tool allows you to make selections in the Arrangement, regardless of Part boundaries. Selected ranges can be moved, cut, copied etc, or processed with various functions. See page 171 in the Getting Started book.
![]() New arrange tool handling. If you want, tools can now work directly on the Track list to change all parts on a Track. For an example, see "Joining all Parts on a Track into one".
New arrange tool handling. If you want, tools can now work directly on the Track list to change all parts on a Track. For an example, see "Joining all Parts on a Track into one".
![]() New Part and Event handling. You can now nudge selected Parts or Events (moving them by the currently set snap value). This can be done by using key commands or by using the Nudge tool in the editors. See "Moving Notes with the Nudge tool" and "Moving an Audio Event by Nudging".
New Part and Event handling. You can now nudge selected Parts or Events (moving them by the currently set snap value). This can be done by using key commands or by using the Nudge tool in the editors. See "Moving Notes with the Nudge tool" and "Moving an Audio Event by Nudging".
![]()
 Extended Arrange window Tool box. The Tool box in the Arrange window has been extended with new tools like direct velocity
and transpose controls (see page 207 in the printed Getting Started book), a stretch tool, a groove tool and a logical preset tool.
Extended Arrange window Tool box. The Tool box in the Arrange window has been extended with new tools like direct velocity
and transpose controls (see page 207 in the printed Getting Started book), a stretch tool, a groove tool and a logical preset tool.
![]() New Key Edit tool handling. The Line tool can now be used on notes to trim the start or end positions of several notes at the same time. See "Resizing multiple notes with the Line tool".
New Key Edit tool handling. The Line tool can now be used on notes to trim the start or end positions of several notes at the same time. See "Resizing multiple notes with the Line tool".
![]() Display resolution up to 15360 ticks per beat. Cubase VST 5.0 offers super high editing resolution for precise positioning of audio events and equally high timing performance with Virtual Instruments or Linear Timebase? MIDI in-terfaces. See page 48 in the printed Getting Started book.
Display resolution up to 15360 ticks per beat. Cubase VST 5.0 offers super high editing resolution for precise positioning of audio events and equally high timing performance with Virtual Instruments or Linear Timebase? MIDI in-terfaces. See page 48 in the printed Getting Started book.
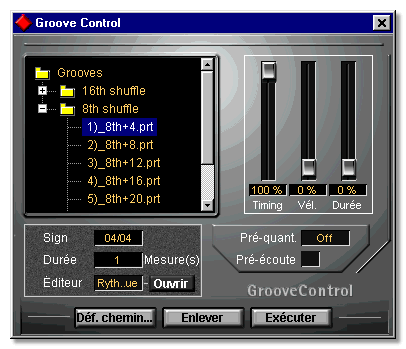
![]() Improved Groove Quantize handling. Grooves can now be more than one bar long, and it is very easy to edit existing Grooves or create your own. By using the Groove Control window, you can specify to what extent the
timing, the velocity profile and duration pattern should be applied. And most importantly, the results of the Groove Quantization can be monitored in real-time! This is described in the chapter "More about Quantizing and Grooves".
Improved Groove Quantize handling. Grooves can now be more than one bar long, and it is very easy to edit existing Grooves or create your own. By using the Groove Control window, you can specify to what extent the
timing, the velocity profile and duration pattern should be applied. And most importantly, the results of the Groove Quantization can be monitored in real-time! This is described in the chapter "More about Quantizing and Grooves".
![]()
 Comprehensive Marker Track system. You can define locations and zones in a Song by creating and naming Marker Parts. The created Marker Parts will automatically be listed on a pop-up menu, available in all Cubase VST
windows, for quick navigation and selection. Read more in the chapter "The Marker Track" on page 185 in the printed Getting Started book.
Comprehensive Marker Track system. You can define locations and zones in a Song by creating and naming Marker Parts. The created Marker Parts will automatically be listed on a pop-up menu, available in all Cubase VST
windows, for quick navigation and selection. Read more in the chapter "The Marker Track" on page 185 in the printed Getting Started book.
![]() New Track column attribute entries. The number of available Track columns has been largely expanded, allowing you to display any of the controls normally shown in the Inspector (for all Tracks instead of just for one
Track at the time). You can also have the Track columns mirror VST mixer settings such as vol-ume
and pan. Track Columns can be hidden and reordered, and any Track Column configuration can be saved as a Track View for instant recall. See page 197 in the Getting Started book and the section "Track Views" in the Getting into the Details document.
New Track column attribute entries. The number of available Track columns has been largely expanded, allowing you to display any of the controls normally shown in the Inspector (for all Tracks instead of just for one
Track at the time). You can also have the Track columns mirror VST mixer settings such as vol-ume
and pan. Track Columns can be hidden and reordered, and any Track Column configuration can be saved as a Track View for instant recall. See page 197 in the Getting Started book and the section "Track Views" in the Getting into the Details document.

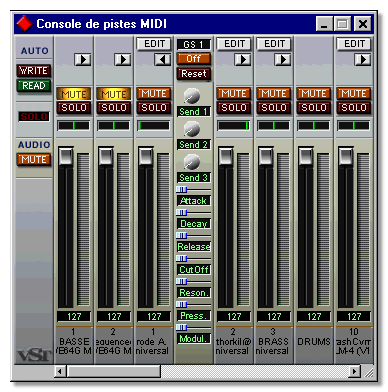
![]() MIDI Track mixer. The MIDI Track mixer allows you to adjust volume, pan, GS/XG effects and other parameters for MIDI Tracks, in an environment similar to the VST mixers. The mixer configures itself ac-cording to the MIDI Tracks in the current arrangement and can be fully automated. You can also create custom mixer panels. This is all described in the chapter "The MIDI Track Mixer".
MIDI Track mixer. The MIDI Track mixer allows you to adjust volume, pan, GS/XG effects and other parameters for MIDI Tracks, in an environment similar to the VST mixers. The mixer configures itself ac-cording to the MIDI Tracks in the current arrangement and can be fully automated. You can also create custom mixer panels. This is all described in the chapter "The MIDI Track Mixer".
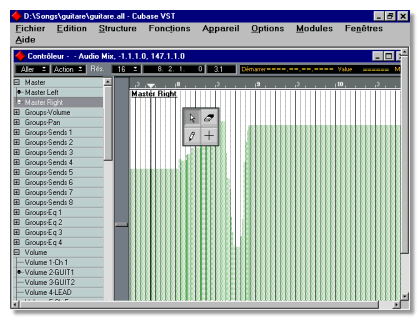
![]() Controller editor. The separate Controller editor offers graphic editing of MIDI controllers, VST automation
data (complete with waveform overview) and all MIDI-Mixer objects. See the chapter "The Controller Editor".
Controller editor. The separate Controller editor offers graphic editing of MIDI controllers, VST automation
data (complete with waveform overview) and all MIDI-Mixer objects. See the chapter "The Controller Editor".
![]() New interaction between Parts and Editors. Editors can remain open and new Parts can be added to the currently opened editor. Parts can be moved while editors are open. See "Opening an Editor".
New interaction between Parts and Editors. Editors can remain open and new Parts can be added to the currently opened editor. Parts can be moved while editors are open. See "Opening an Editor".
![]() Additional real-time non-destructive play parameters. The Inspector for MIDI Tracks now has an extended area with the following new parameters :
Additional real-time non-destructive play parameters. The Inspector for MIDI Tracks now has an extended area with the following new parameters :
- Randomize length/position/velocity/pitch
- MIDI velocity limit
- MIDI velocity filter
- MIDI velocity optimize
- MIDI note limit
- MIDI note filter
![]() Multiple ghost-outputs for MIDI Tracks. Any MIDI Track can have additional ghost-outputs. Each additional output has its own MIDI channel and output selection and a full set of Inspector parameters, including the new MIDI note limit parameter, allowing for complex split output devices. See "Using the Multi Out feature".
Multiple ghost-outputs for MIDI Tracks. Any MIDI Track can have additional ghost-outputs. Each additional output has its own MIDI channel and output selection and a full set of Inspector parameters, including the new MIDI note limit parameter, allowing for complex split output devices. See "Using the Multi Out feature".
![]() The Score editor hugely expanded (Cubase VST Score and Cubase VST/32 only). The score editing, layout and printing options have been given a major update, adding over 300 new score features ! These are covered in the separate document "Score Printing and Layout".
The Score editor hugely expanded (Cubase VST Score and Cubase VST/32 only). The score editing, layout and printing options have been given a major update, adding over 300 new score features ! These are covered in the separate document "Score Printing and Layout".
![]() Thousands of MIDI mixer objects. The number of MIDI mixer objects has been increased from the original 128, and there are also new object types. See "The MIDI Mixer and Mix Tracks".
Thousands of MIDI mixer objects. The number of MIDI mixer objects has been increased from the original 128, and there are also new object types. See "The MIDI Mixer and Mix Tracks".





